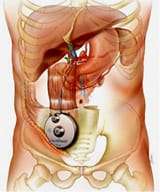
The experts at the UPMC Liver Cancer Center often use intrahepatic pump therapy to treat hepatic (liver) metastases from colorectal cancer.
This allows us to administer a much higher concentration of the chemotherapy where you need it most — directly on the liver tumor itself.
Who we Treat
People who most benefit from intrahepatic pump therapy include those who have:
- Inoperable metastatic colon cancer to the liver who have failed standard chemotherapy
- Had cancer resected or removed from the liver, but are at high risk for developing further liver cancers because microscopic cancer cells likely remain within the liver
Contact the UPMC Liver Cancer Center
To schedule an appointment, or for more information, call the UPMC Liver Cancer Center at 412-692-2001.
Benefits of Intrahepatic Pump Therapy
Fewer side effects
By administering the chemotherapy directly into the liver, we can use a much higher concentration of the chemotherapy with fewer systemic side effects.
Higher response rate
Particularly for colon cancer metastases to the liver, there is evidence for a higher response rate in patients treated with the chemotherapy drug FUDR® (floxuridine) delivered by an implanted hepatic artery pump.
Lower recurrence rate
Recent publications have shown that patients who have this form of chemotherapy after surgical resection of tumor metastases from the liver, are much less likely for tumor recurrence than patients who are not treated this way.
What to Expect
Overview
- You will have an operation to surgically place the pump under your skin, below your ribs.
- The pump has thin tubing that goes into a side branch of the hepatic (liver) artery and delivers chemotherapy (or saline) directly into the liver.
- Two weeks after surgery, the chemotherapy treatment begins.
Length of procedure
Length of hospital stay
Surgical Placement of the Intrahepatic Pump
A surgeon from the Liver Cancer Center will:
- Make an incision on the right side of your abdomen under your ribs
- Place a small metal pump (about 3 inches in size) in a pocket under your skin
- Guide the thin tubing from the pump into a side branch of the hepatic artery
- Fill the pump with heparinized saline, so the tubing does not clot off